Citations Report
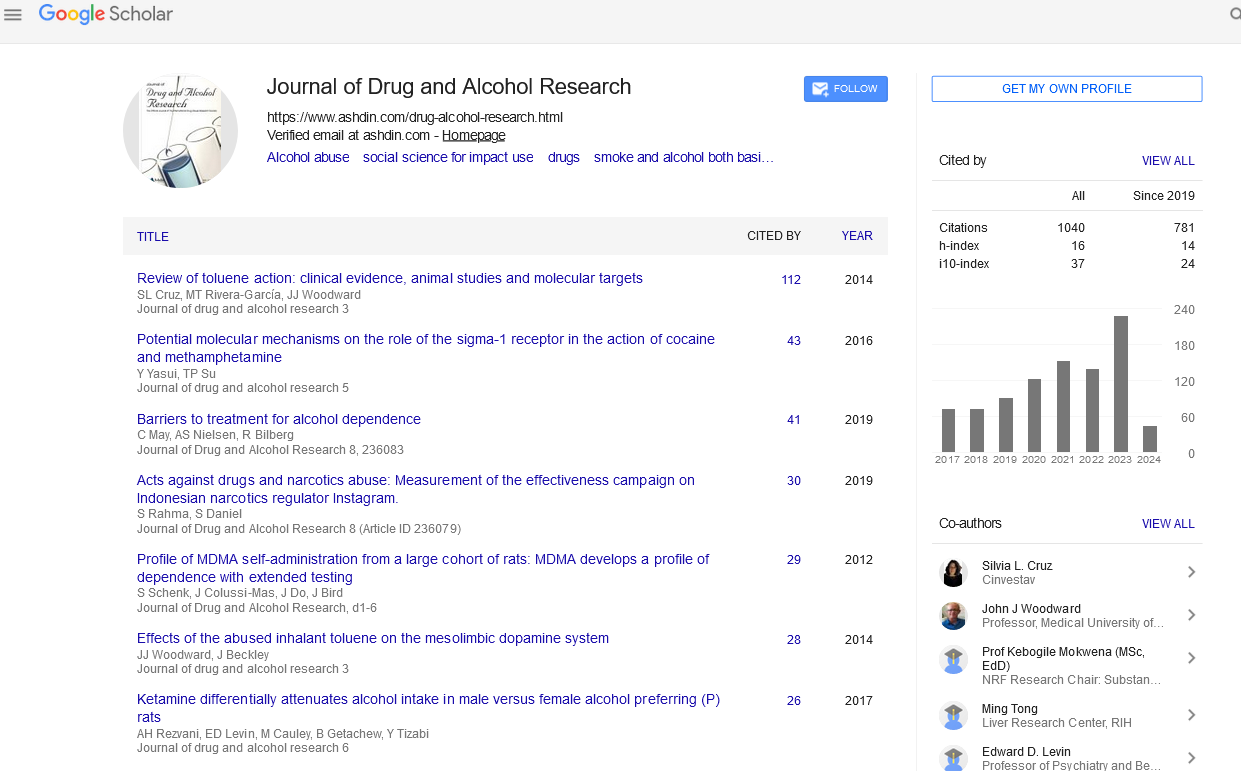
Journal of Drug and Alcohol Research : Citations & Metrics Report
Articles published in Journal of Drug and Alcohol Research have been cited by esteemed scholars and scientists all around the world. Journal of Drug and Alcohol Research has got h-index 16, which means every article in Journal of Drug and Alcohol Research has got 16 average citations.
Following are the list of articles that have cited the articles published in Journal of Drug and Alcohol Research.
| 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Total published articles |
60 | 60 | 60 | 57 | 28 | 20 |
Research, Review articles and Editorials |
40 | 58 | 59 | 53 | 38 | 21 |
Research communications, Review communications, Editorial communications, Case reports and Commentary |
0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Conference proceedings |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Citations received as per Google Scholar, other indexing platforms and portals |
167 | 241 | 141 | 157 | 124 | 91 |
| Journal total citations count | 1127 |
| Journal impact factor | 3.09 |
| Journal 5 years impact factor | 3.28 |
| Journal cite score | 3.16 |
| Journal h-index | 16 |
| Journal h-index since 2019 | 14 |
Repeated administration of the 5-HT1B/1A agonist, RU 24969, facilitates the acquisition of MDMA self-administration: role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptor |
|
High ambient temperature facilitates the acquisition of 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) self-administration |
|
Comparison of the effects of abstinence on MDMA and cocaine self-administration in rats |
|
Regional changes in? FosB expression in rat brain following MDMA self?administration predict increased sensitivity to effects of locally infused MDMA |
|
The Role of Serotonin in MDMA Self-administration in rats |
|
MDMA self-administration fails to alter the behavioral response to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists |
|
The effect of MDMA self-administration on MDMA-produced hyperactivity and c-fos expression |
|
The Role of the Serotonin Transporter as a Genetic Risk Factor in the Development of Drug Addiction |
|
A Molecular Mechanism of MDMA Dependence |
|
Effect of repeated MDMA exposure on rat brain and behaviour |
|
Repeated administration of the 5-HT agonist, RU 24969, facilitates the acquisition of MDMA self-administration: role of 5-HT and 5-HT receptor mechanisms. |
|
Repeated MDMA administration increases MDMA-produced locomotor activity and facilitates the acquisition of MDMA self-administration: role of dopamine D2 |
|
Serotonin antagonists fail to alter MDMA self-administration in rats |
|
One day access to a running wheel reduces self-administration of D-methamphetamine, MDMA and methylone |
|
Predicting the abuse liability of entactogen-class, new and emerging psychoactive substances via preclinical models of drug self-administration |
|
Effects of ??pyrrolidinopentiophenone and 4-methyl-n-ethylcathinone, two synthetic cathinones commonly found in second-generation “bath salts,” on intracranial self … |
|
Intravenous self-administration of entactogen-class stimulants in male rats |
|
A genetic deletion of the serotonin transporter greatly enhances the reinforcing properties of MDMA in rats |
|
The reinforcing and rewarding effects of methylone, a synthetic cathinone commonly found in “bath salts” |
|
Intravenous self-administration of mephedrone, methylone and MDMA in female rats |
|